Precision in Practice
Technology-driven methodologies from the foundation of our research, anchored by four key pillars: MRI image processing, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and neuromodulation.

Precision in Practice
Technology-driven methodologies from the foundation of our research, anchored by four key pillars: MRI image processing, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and neuromodulation.
MRI processing in brain research involves studying patterns of brain connectivity to better understand mental disorders and cognitive impairment. By analyzing detailed magnetic resonance imaging data, researchers can uncover structural and functional brain changes, offering insights into disease mechanisms and advancing the development of targeted therapies and interventions. This powerful technique is a cornerstone of neuroscience research.
LEARN MORE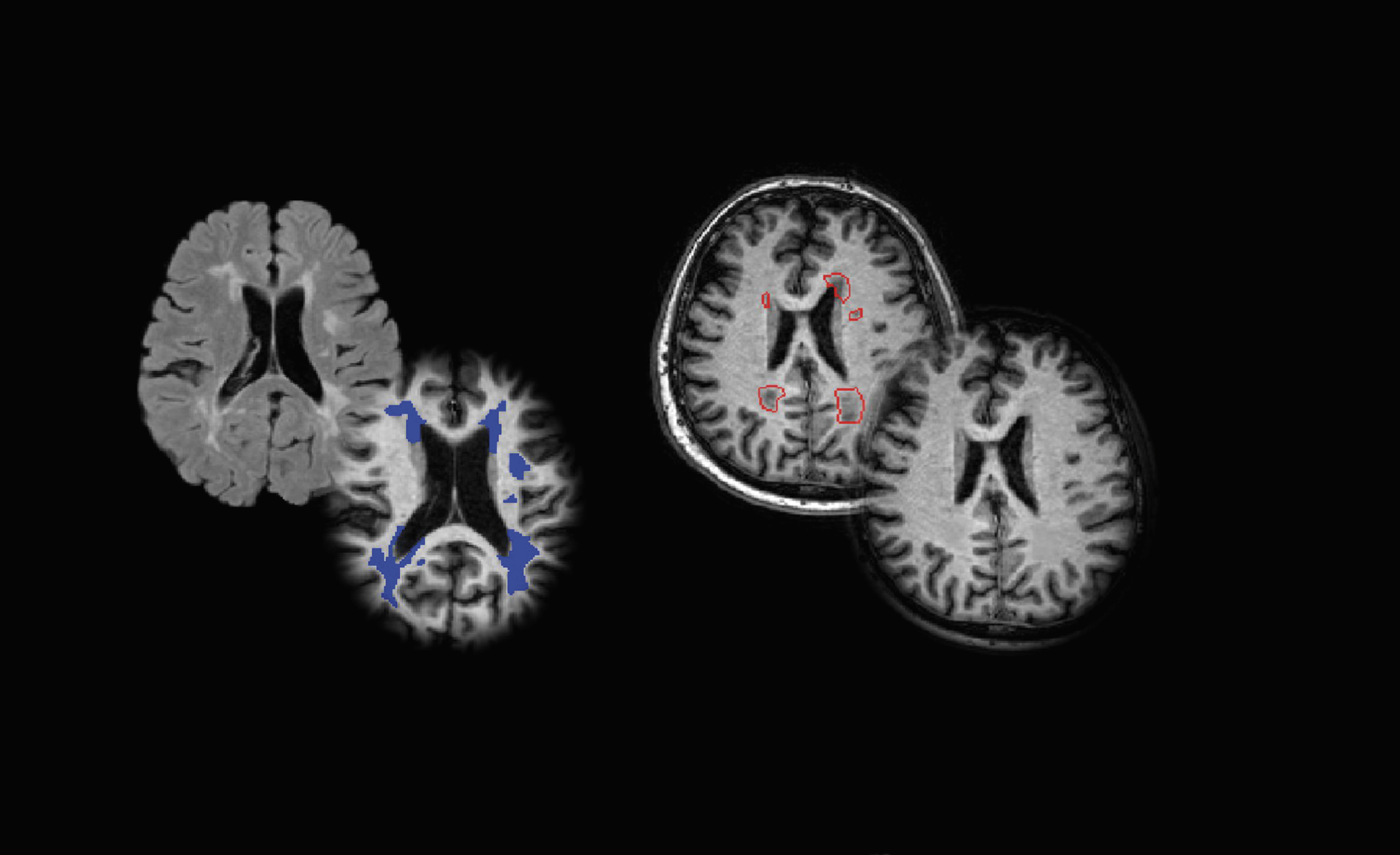
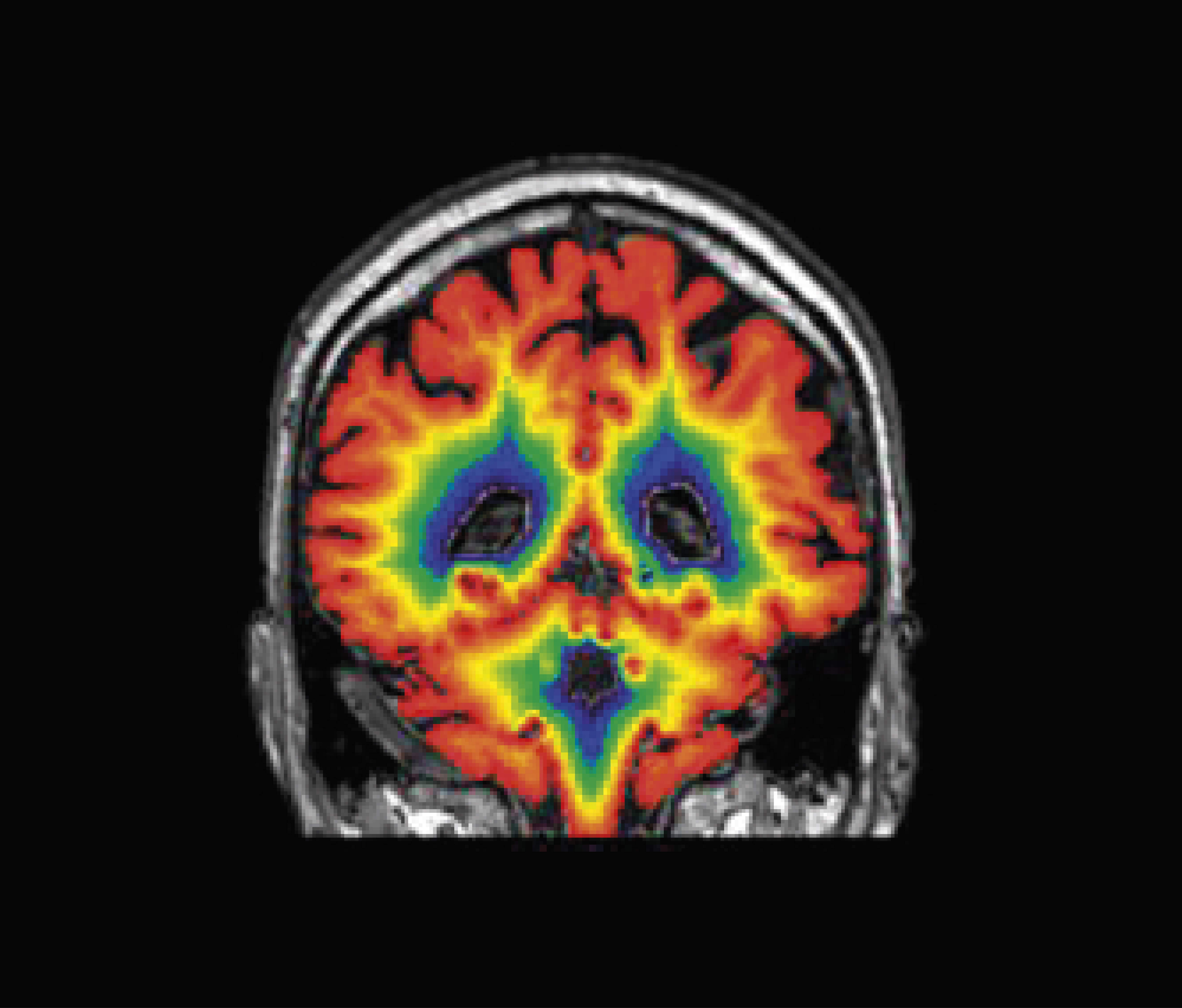
Next-generation biomarkers are advanced biological indicators that leverage cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and high-dimensional data analysis to detect and monitor diseases with greater precision. These innovative biomarkers go beyond traditional methods, providing deeper insights into disease mechanisms, enabling earlier diagnosis, and guiding personalized treatments. They represent a transformative step in advancing healthcare and improving patient outcomes.
LEARN MOREData analysis in research involves extracting meaningful insights from complex datasets to answer scientific questions and uncover hidden patterns. By applying statistical methods, computational tools, and machine learning techniques, researchers can interpret results, validate hypotheses, and generate predictive models. This approach is essential for driving innovation, improving decision-making, and advancing knowledge across diverse fields of study.
LEARN MORE
Artificial intelligence (AI) applied to neuropsychology and neuropsychiatry leverages advanced algorithms to analyze complex brain data, identify patterns, and predict outcomes with unprecedented accuracy. By integrating AI into these fields, our research group develops innovative tools to enhance diagnosis, monitor disease progression, and personalize treatments for cognitive and mental health disorders, paving the way for more effective, data-driven clinical care.
Non-invasive neuromodulation is a cutting-edge technique that uses external stimulation to influence brain activity without the need for surgery or implants. By applying targeted magnetic or electrical pulses, this approach can modulate neural pathways, improving cognitive, emotional, or motor functions. At our research group, we harness neuromodulation to study and develop innovative therapies for neurological disorders, addictions, and cognitive decline, offering new possibilities for non-pharmacological and patient-centered treatments.
